Oil Distillation Plant
- Commodity name: Oil Distillation Plant
- Capacity Model: 5TPD,10TPD, 30TPD, 50TPD, 100TPD,250TP,300TPD
- Raw material: Bilge Oil, Used Engine Oil, Black Oil, Waste Hydraulic Oil, Heavy Oil, Fuel Oil, Pyrolysis Oil, Oil Sludge, Other Waste Oil,etc...
- End Production: Euro III standard Diesel, Residue Oil; different raw material produce different yield, diesel, base oil, gasoline
Category:
Details
Product Description
Oil distillation plant is to separate black oil/used oil/waste engine oil etc. into its different components based on their boiling points through a process called fractional distillation. This machine is an equipment with additives to improve the oil quality such as odour, color after the catalytic run refining process.
Different input materials

End Products

|
No.
|
End Production
|
Yield
|
Usage
|
|
1
|
Diesel
|
73%
|
Used for diesel engine, ship, tractors, forklift, agriculture machinery or say low-speed motor
|
|
2
|
Gasoline
|
12%
|
Used for gasoline engine
|
|
3
|
Residue Oil
|
9%
|
Feeding into pyrolysis machine for heating, or selling directly for making building road
|
|
4
|
Non-Condensible Gas
|
3%
|
Recycle as heating fuel after treated by gas-treatment system
|
Layout Drawing
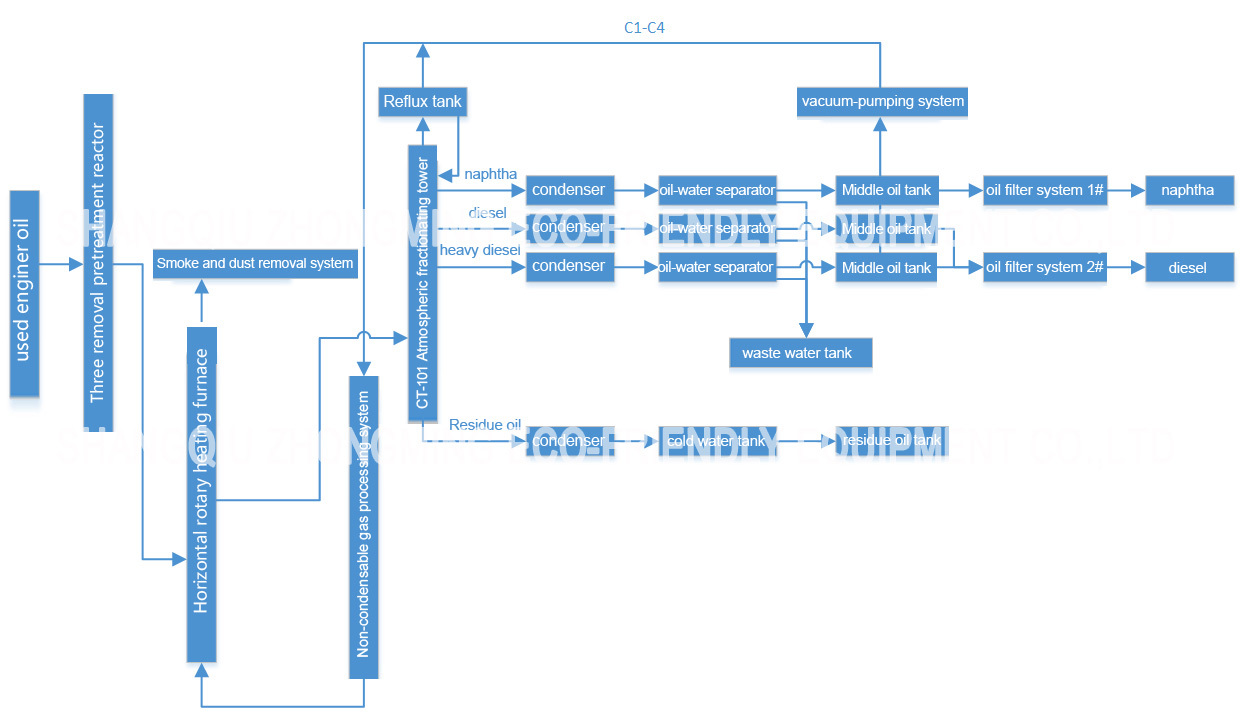
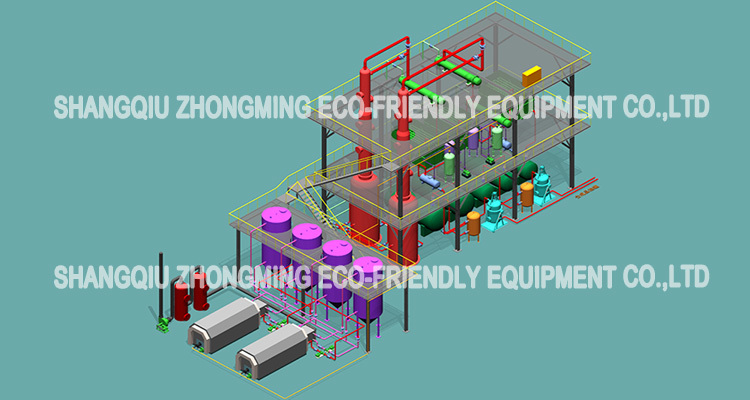
This used/waste oil distillation plant involves heating the used/waste oil to separate the various components based on their different boiling points which allows for the recovery of valuable lubricating oil fractions while removing impurities and contaminants.
Below is a basic overview of the typical steps involved in a used/waste oil distillation plant:
1.Pre-treatment:
Used/waste oil contains impurities such as water, sludge or solids particles . Before distillation, the used/waste oil may undergo pre-treatment process like filtration and settling to remove the impurities.
2. Heating:
The pre-treated used/waste oil is heated in a distillation kettle, the heat causes the oil vaporize, and different fractions evaporated at different temperatures based on different boiling points.
3. Fractionation:
The vaporized oil is condensed back into liquid form. The different fractions can be collected separately, allowing for the separation of various components such as base oil, diesel and other lighter hydrocarbons.
4. Cooling & condensation:
The vaporized oil is cooled, and the resulting condensate is collected in separate containers which allows for the recovery of different fractions with specific properties.
5. Collection & storage:
The recovered based oil and other fractions can be collected and stored for further processing or distribution.
6. Residue handling:
The residue or heavier fractions that do not vaporize during distillation may require proper proposal or further treatment.
One more point, the specific design and operational details of used/waste oil distillation plants can vary, and some projects may include additional steps or technologies to enhance the efficiency of process and meet the specific product quality standards.
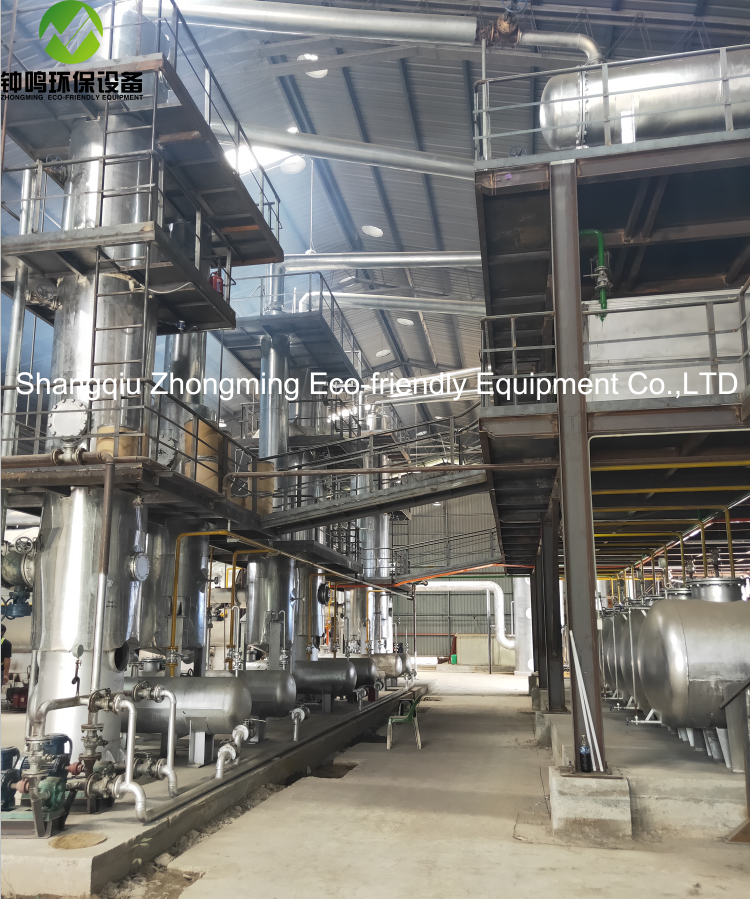

Project Case
https://www.tiktok.com/t/ZP8r2SwGN/
https://www.tiktok.com/t/ZP8r2AUeo/
Key words:
Related Products
Inquiry
*Note: Please be sure to fill in the information accurately and keep the communication open, we will get in touch with you as soon as possible







